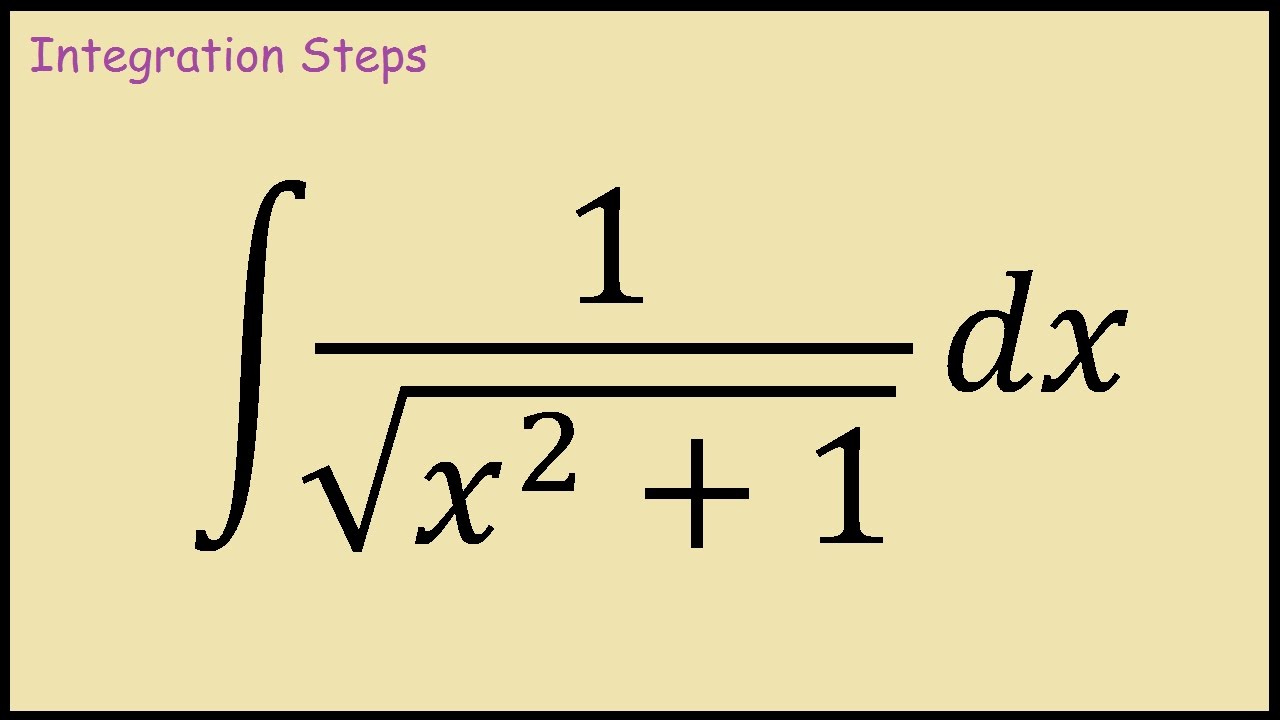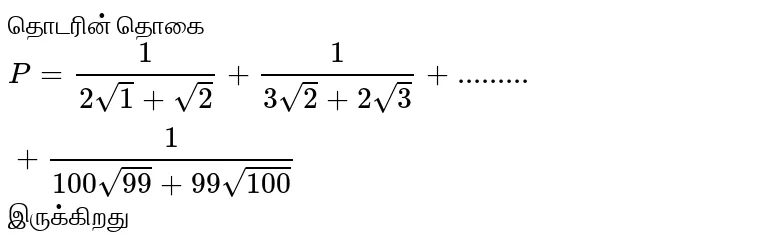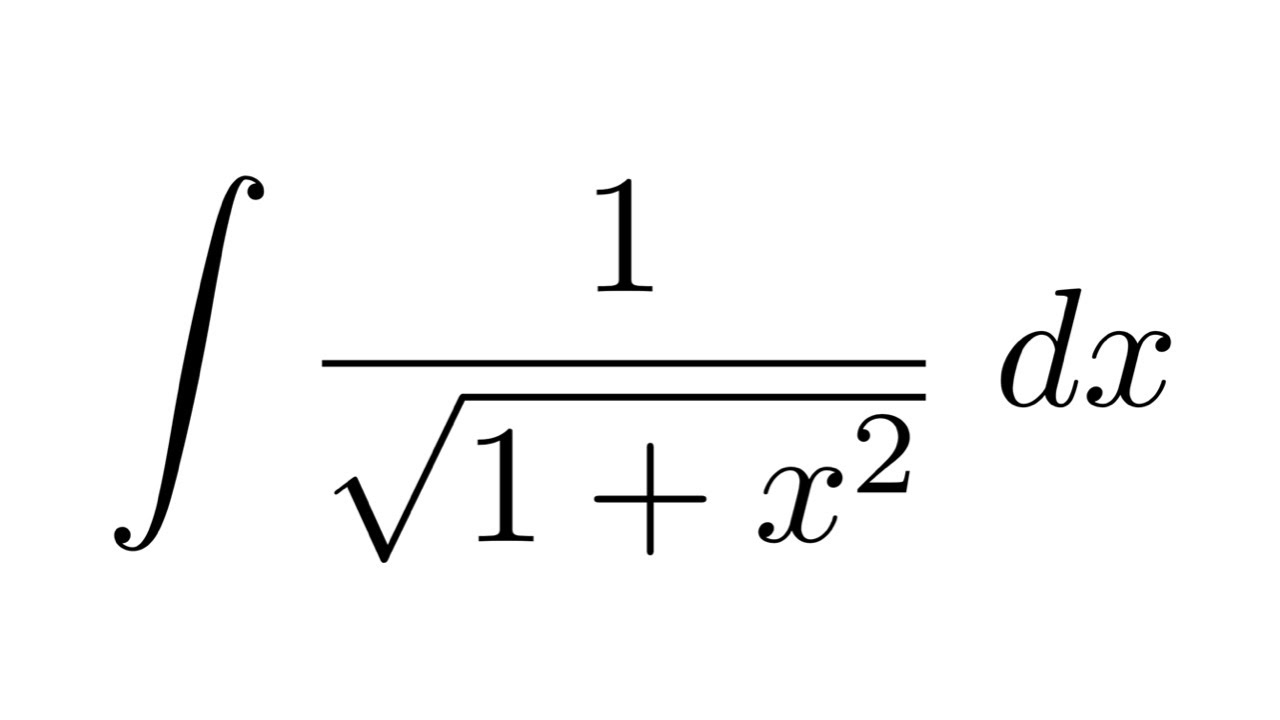Calculating 1/(2+Sqrt(5)) + 1/(2-Sqrt(5)) should return -4 · Issue #125 · axkr/symja_android_library · GitHub

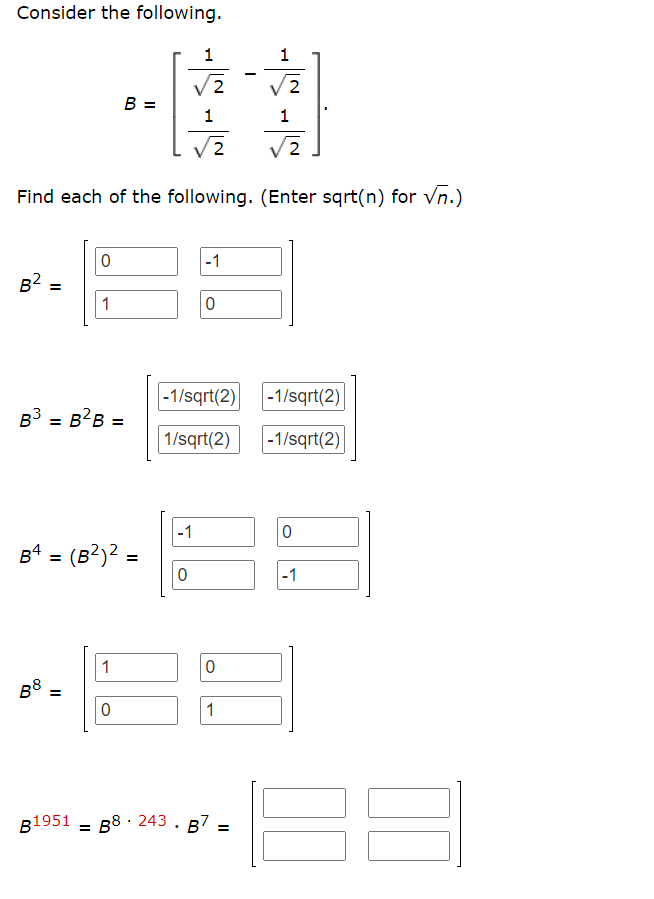
IF x =(4sqrt(2))/{sqrt(2)+1} Then find 1/sqrt(2){((x+2)/(x-2) ) +((x + 2sqrt(2))/(x - 2sqrt(2)))}? | Socratic
![1 + sqrt { 2 } ) (viii) ( frac { 1 + sqrt { 2 } } { 2 - sqrt { 2 } } quad ( 2014 ] quad ( i x ) frac { 3 - 2 sqrt { 2 } } { 3 + 2 sqrt { 2 } } ) ( = 1.414 , sqrt { 3 } = 1.732 , sqrt { 5 } = 2.236 ) and ( sqrt { 10 } = 3.162 ) laces of decimais, of ... 1 + sqrt { 2 } ) (viii) ( frac { 1 + sqrt { 2 } } { 2 - sqrt { 2 } } quad ( 2014 ] quad ( i x ) frac { 3 - 2 sqrt { 2 } } { 3 + 2 sqrt { 2 } } ) ( = 1.414 , sqrt { 3 } = 1.732 , sqrt { 5 } = 2.236 ) and ( sqrt { 10 } = 3.162 ) laces of decimais, of ...](https://toppr-doubts-media.s3.amazonaws.com/images/10041366/d3fa63f6-166b-4675-aaea-ab7028ac7fc5.jpg)
1 + sqrt { 2 } ) (viii) ( frac { 1 + sqrt { 2 } } { 2 - sqrt { 2 } } quad ( 2014 ] quad ( i x ) frac { 3 - 2 sqrt { 2 } } { 3 + 2 sqrt { 2 } } ) ( = 1.414 , sqrt { 3 } = 1.732 , sqrt { 5 } = 2.236 ) and ( sqrt { 10 } = 3.162 ) laces of decimais, of ...
s=√(3n+2)+√(3n) , n∈ N, then s is 1. always rational 2. rational for 2 values of n 3. always irrational 4.rational for a unique value of N
![1 + sqrt { 2 } ) (viii) ( frac { 1 + sqrt { 2 } } { 2 - sqrt { 2 } } quad ( 2014 ] quad ( i x ) frac { 3 - 2 sqrt { 2 } } { 3 + 2 sqrt { 2 } } ) ( = 1.414 , sqrt { 3 } = 1.732 , sqrt { 5 } = 2.236 ) and ( sqrt { 10 } = 3.162 ) laces of decimais, of ... 1 + sqrt { 2 } ) (viii) ( frac { 1 + sqrt { 2 } } { 2 - sqrt { 2 } } quad ( 2014 ] quad ( i x ) frac { 3 - 2 sqrt { 2 } } { 3 + 2 sqrt { 2 } } ) ( = 1.414 , sqrt { 3 } = 1.732 , sqrt { 5 } = 2.236 ) and ( sqrt { 10 } = 3.162 ) laces of decimais, of ...](https://toppr-doubts-media.s3.amazonaws.com/images/2330140/19871c07-b2fd-4ed8-aba4-c4db990c462d.jpg)


![How to rationalize [math] \frac{1}{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3} + \sqrt{5}}[/math] - Quora How to rationalize [math] \frac{1}{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3} + \sqrt{5}}[/math] - Quora](https://qph.cf2.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-570ea014b1464fe5c16c010d47b54e0e.webp)